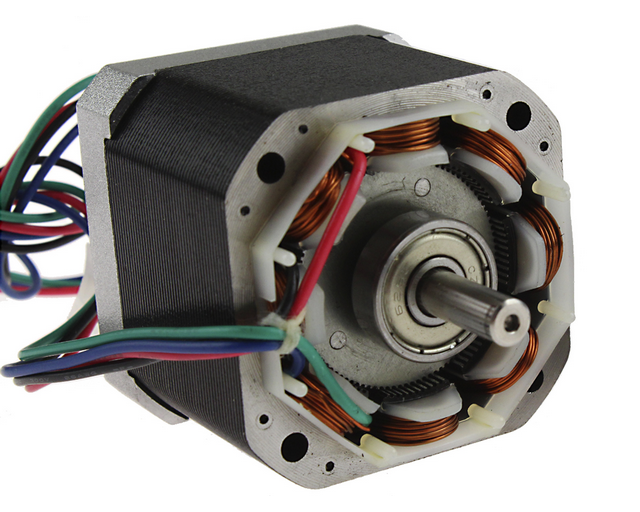
Stepper Motor

Ms.A. Akshaya
""
ABOUT
rotation. Every revolution of the stepper motor is divided into a discrete number of steps and the motor must be sent a separate pulse for each step. The stepper motor can only take one step at a time and each step is the same size. The motor’s position can be controlled without any feedback mechanism.
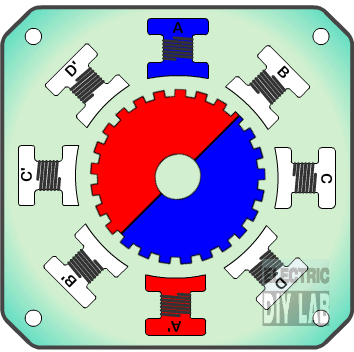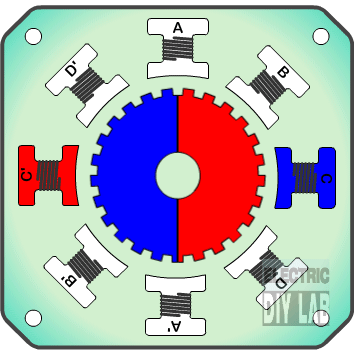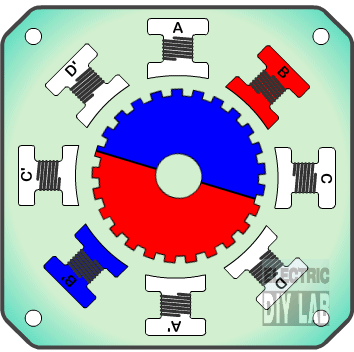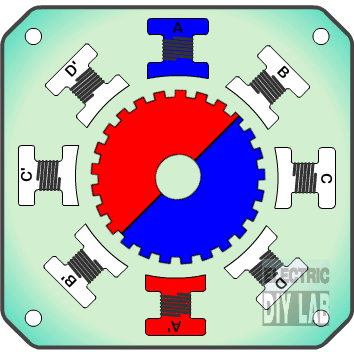
» Frame 1: The top electromagnet (1) is turned on, attracting the nearest teeth of the gear-shaped iron rotor. With the teeth aligned to electromagnet 1, they will be slightly offset from the right electromagnet (2).
» Frame 2:The top electromagnet (1) is turned off, and the right electromagnet (2) is energized, pulling the teeth into alignment with it. This results in a rotation of 3.6° in this example.
» Frame 3:The bottom electromagnet (3) is energized; another 3.6° rotation occurs.
» Frame 4: The left electromagnet (4) is energized, rotating again by 3.6°. When the top electromagnet (1) is again enabled, the rotor will have rotated by one tooth position; since there are 25 teeth, it will take 100 steps to make a full rotation in this example.
Fundamentals of operation:
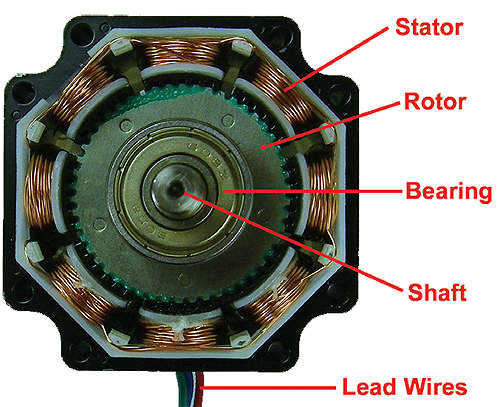
Brushed dc motor rotates continuously when DC Voltage is applied to their terminals. The stepper motor is known by its property of converting a train of input pulses (typically square wave pulses) into a precisely defined increment in the shaft position. Each pulse moves the shaft through a fixed angle. Stepper motors effectively have multiple “toothed” electromagnets arranged around a central gear-shaped piece of iron. The electromagnets are energized by an external driver circuit. To make the motor shaft turn, first, one electromagnet is given power, which magnetically attracts the gear’s teeth. When the gear’s teeth are aligned to the first electromagnet, they are slightly offset from the next electromagnet. This means that when the next electromagnet is turned on and the first is turned off, the gear rotates slightly to align with the next one. From there the process is repeated. Each of those rotations is called a “step”, with an integer number of steps making a full rotation. In that way, the motor can be turned by a precise angle. The circular arrangement of electromagnets is divided into groups, each group called a phase, and there is an equal number of electromagnets per group. The number of groups is chosen by the designer of the stepper motor.
Working principle
» The stepper motor rotor is a permanent How does a stepper motor work? The stepper motor rotor is a permanent magnet, when the current flows through the stator winding, the stator winding to produce a vector magnetic field.
» The magnetic field drives the rotor to rotate by an angle so that the pair of magnetic fields of the rotor and the magnetic field direction of the stator are consistent. When the stator’s vector magnetic field is rotated by an angle, the rotor also rotates with the magnetic field at an angle. Each time an electrical pulse is input, the motor rotates one degree further.
» The angular displacement it outputs is proportional to the number of pulses input and the speed is proportional to the pulse frequency. Change the order of winding power, the motor will reverse. Therefore, it can control the rotation of the stepping motor by controlling the number of pulses, the frequency and the electrical sequence of each phase winding of the motor. Winding, the stator winding to produce a vector magnetic field.
» The magnetic field drives the rotor to rotate by an angle so that the pair of magnetic fields of the rotor and the magnetic field direction of the stator are consistent. When the stator’s vector magnetic field is rotated by an angle, the rotor also rotates with the magnetic field at an angle. Each time an electrical pulse is input, the motor rotates one degree further. The angular displacement it outputs is proportional to the number of pulses input and the speed is proportional to the pulse frequency.
» Change the order of winding power, the motor will reverse. Therefore, it can control the rotation of the stepping motor by controlling the number of pulses, the frequency and the electrical sequence of each phase winding of the motor.
Types :
» Permanent Magnet Stepper Motor (PM)PM stepper motor- use a permanent magnet(PM) in the rotor and operate on the attraction or repulsion between the rotor PM and the stator electromagnets. generally 2-phase, with small torque and volume; its stepping angle is generally 7.5° or 15°.
» Variable Reluctance Stepper Motor (VR)VR stepper motor -is generally 3-phase,high torque output can be realized; the stepping angle is generally 1.5, but the noise and vibration is large; the rotor magnetic circuit of VR stepper motor is made of soft magnetic materials. There is a multi-phase exciting winding on the rotor. The torque is generated by taking advantage of the change in magnetic conductance.
» Hybrid Stepper Motor (HB)HB stepper motor-indicating mixing the advantages of PM and VR is divided into 2-phase, 3-phase, and 5-phase. The stepping angle of 2-phase is generally 1.8°, that of 3-phase 1.2°, and that of 5-phase is 0.72°. It is most widely applied.